Chayote - Chow Chow
Subcribe to back in stock notification
Country of Origin - Mesoamerica
Average Weight - 318 Grams
Introduction
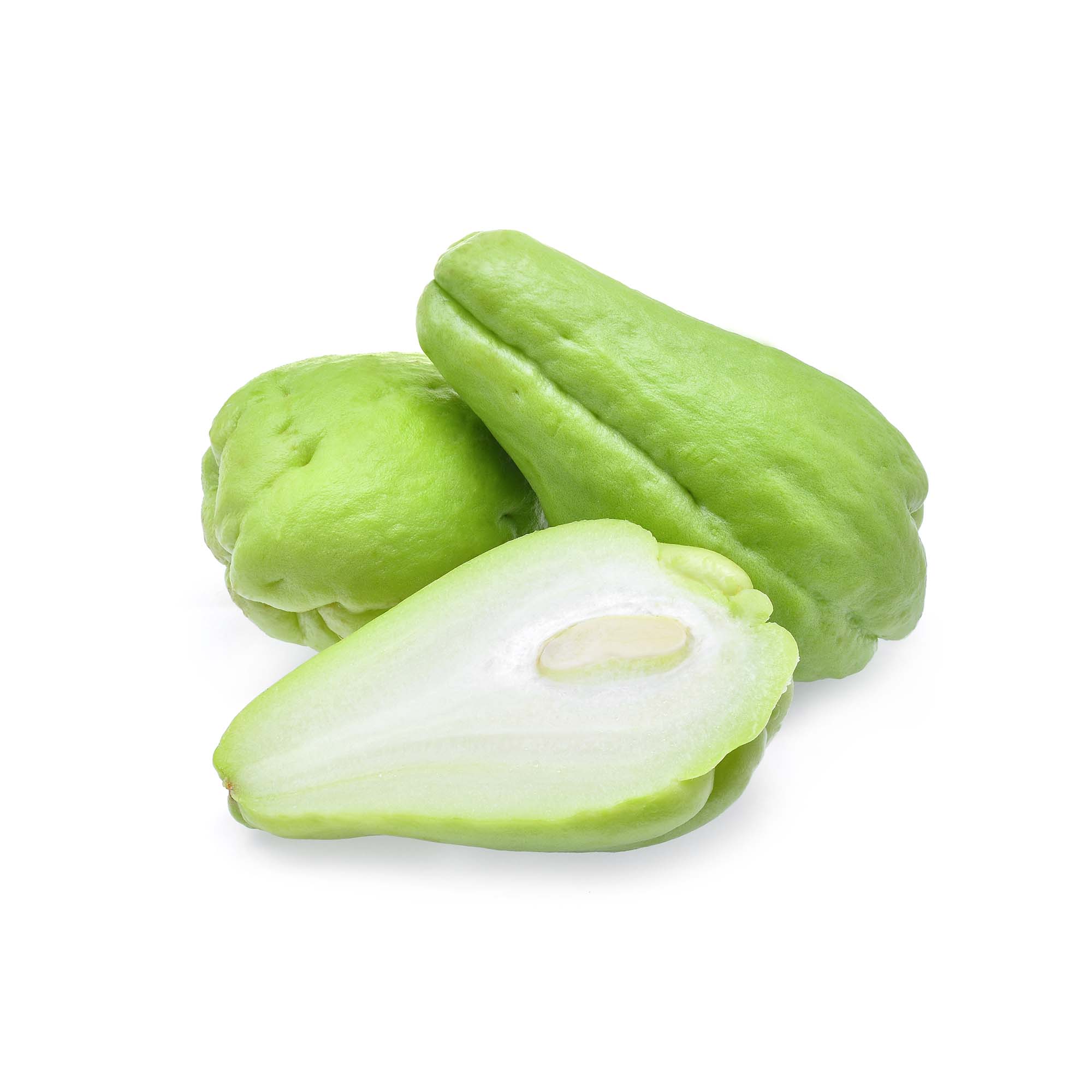
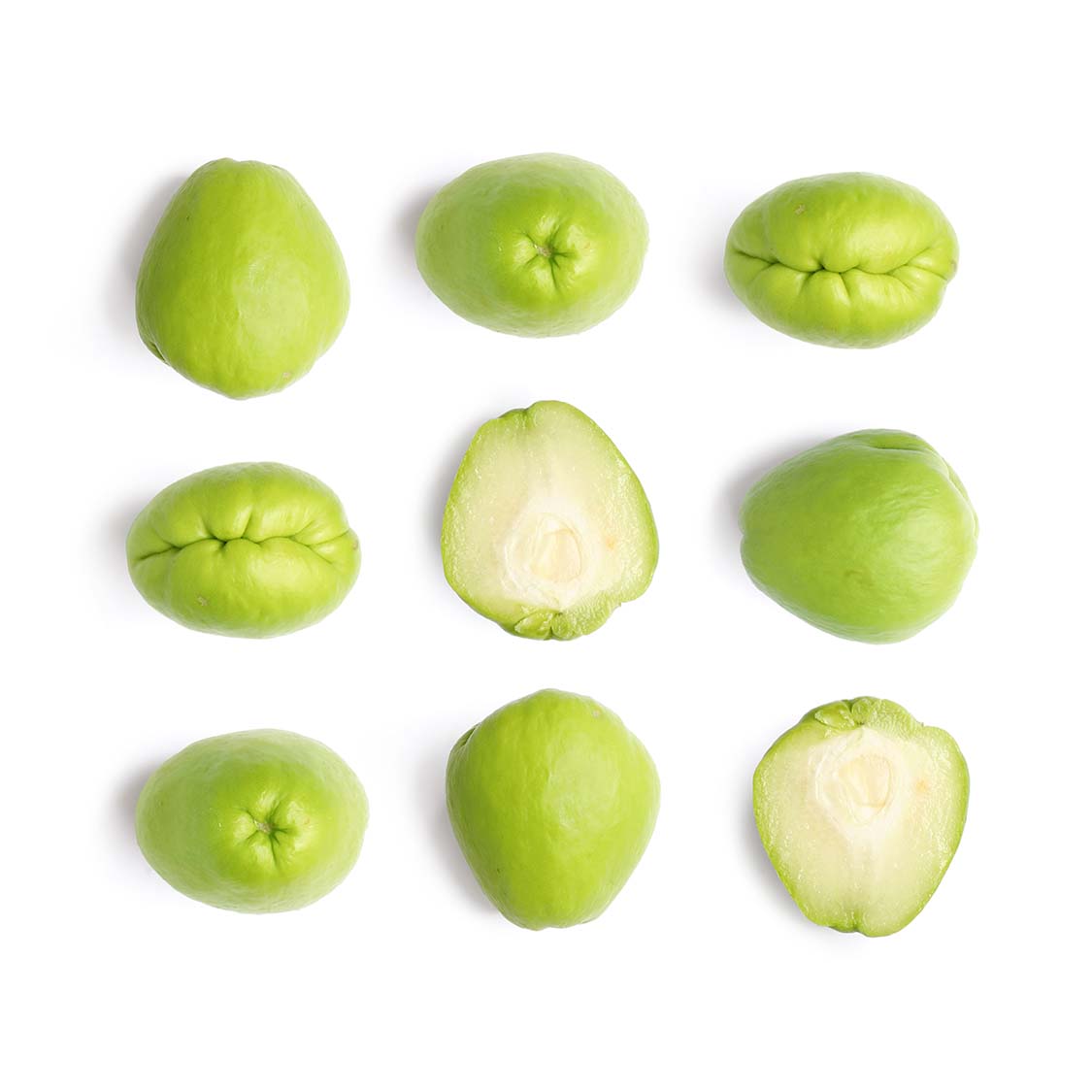
Chayote (Sechium edule) is an edible plant belonging to the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. The fruit is mostly used cooked and it is considered a fruit much like tomato. In terms of its appearance it is pear shaped, lumpy with green colour. However, chayote proves that you should not judge a food by its appearance as it has a very good nutrition profile.
History
The fruit is native to Mesoamerica and was gradually spread into many Latin American countries. There is evidence that chayote was cultured by the Aztecs and Mayans and later European colonists introduced the fruit to the Caribbean, South America, and Europe. Eventually, it was also introduced to Africa, Asia, and Australia.
Regions
Chayote is produced in many regions around the globe. It is produced in high amounts in China, India, Taiwan, California, Florida, Mexico, Italy, Brazil, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Australia and Honduras to name a few.
Flavours & Texture
Its flavour is subtle, something like that of a mildly sweet apple, but mixed with cucumber. In terms of its texture, it is described as a cross between a potato and a cucumber.
Preparation
Chayote can be eaten both raw and cooked. If you want to cook it you can cut it thin and light cook it, stir-fry, or even roast it. You can use it in your salad or you can add it in certain dishes.
Nutritional Value
Chayote is very low in calories, low in fats and it is a good source fiber and minerals.
|
Calories per 100 g |
19 kcal |
|
Fat |
0.1 g |
|
Carbohydrates |
4.5 g |
|
Fiber |
1.7 g |
|
Protein |
0.8 g |
|
Calcium |
1 % of the RDI |
|
Potassium |
3 % of the RDI |
|
Iron |
2 % of the RDI |
SHIPPING
Choose your desired delivery date at the checkout, available delivery dates will be displayed at checkout stage. All orders are dispatched on a 24hr Next Working Day service. If no date is selected your order will be dispatched at the next available date.
We offer Free Next Working Day Delivery on all orders over £75 including our selection boxes.
Our shipping rates are as follows:-
England - £6.95
Scotland - £11.95
Northern Ireland - Not currently available
Customers are responsible for being present at the shipping address provided on the date selected at checkout. Exotic Fruits are not responsible for any missed or attempted deliveries that must be rearranged by the customer.
All orders are packed in cardboard boxes with a biodegradable packing pellets, straw, or hay to protect the fruit during transit.
RETURNS
Let's start by stating the obvious. Since our produce is perishable we cannot accept returns.
That said, we want every customer to be happy so we do offer vouchers, refunds and replacements at our sole discretion if your fruit has arrived inedible. If you would like to report an item which has become damaged or perished during transit, please:- We are not responsible for products that spoil if there is not someone to receive your delivery on the date that you request it, full tracking is provided and can be requested anytime after dispatch.