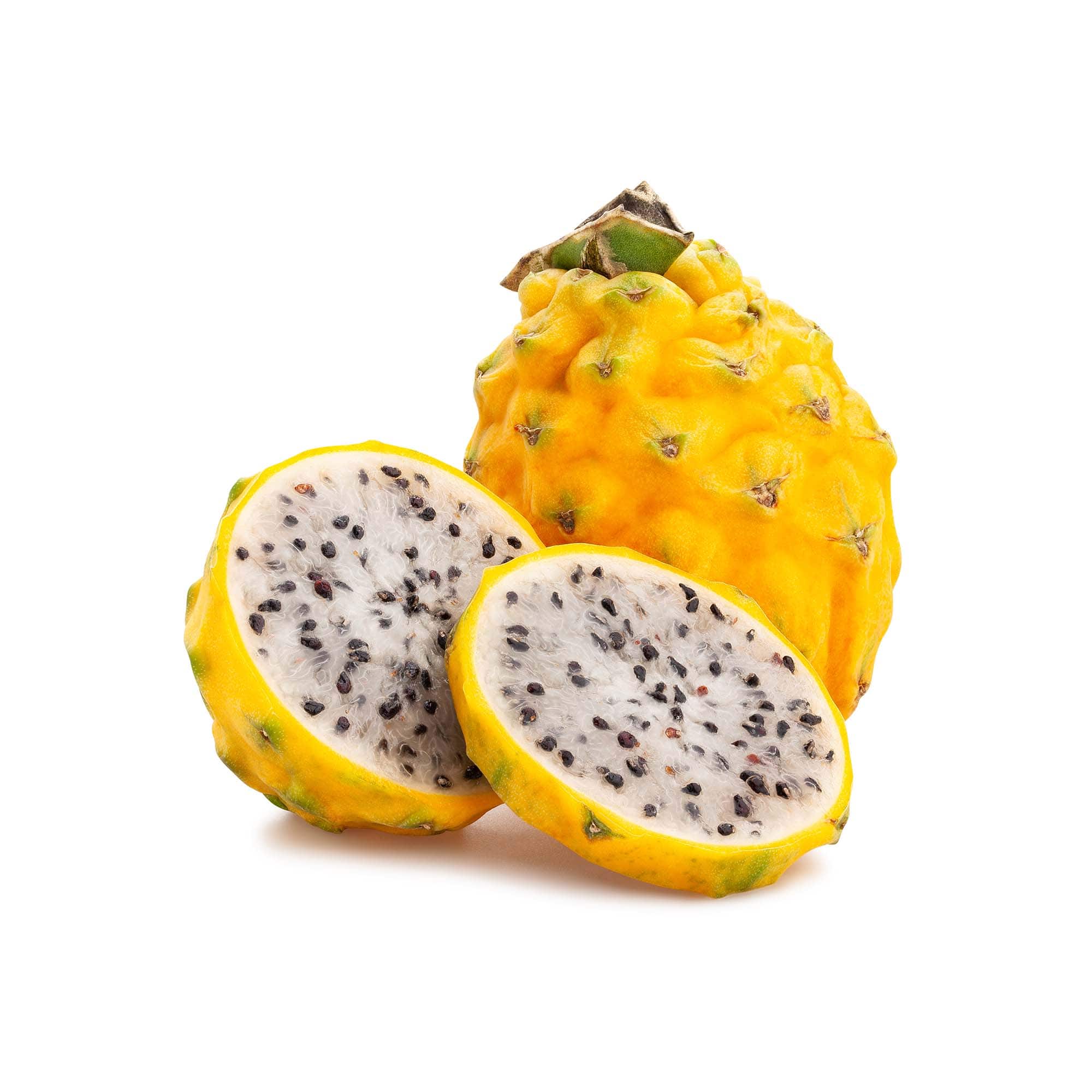
Dragon Fruit - Yellow Pitahaya
Origin - South America
Class - CAT 1
Approx Unit Weight - 250 grams each
Introduction
The dragon fruit is actually a species of cactus which is indigenous to the Americas. It is classified within the broad category of pitaya or pitahaya which also belong to the family Cactaceae. Dragon fruits are a distinct category of pitaya known as the sweet pitaya and they are different compared to sour pitaya variety both in taste and in texture. Sweet pitaya come in three types known as white-fleshed pitaya, red-fleshed pitaya and yellow pitaya. The yellow pitaya (Hylocereus megalanthus) is believed to have the largest flowers of all cacti and as the name implies it has a distinctive yellow fruit.
History
It originated from America and specifically it is native in the areas of Peru, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, and Bolivia. The fruits are still cultivated there and exported all over the world with Colombia being the largest producer.
Regions
Apart from the South American areas, the fruit has been introduced in the USA and it is now cultivated in southern California and in Florida.
Flavours & Texture
Its flavour is mild and sweet with some floral notes and it resembles the taste of kiwifruit or cactus pear. Many people believe that it has the sweetest and finest taste of all pitaya. Its flesh also has a slight crunch but it is softer when compared to watermelon.
Preparation
Upon receipt we recommend keeping in the refrigerator to prolong its best before date. The outer rind is not edible and whilst it does start to perish from where it has been picked, It does a great job of protecting the edible and supers sweet flesh inside. You can cut it in half lengthwise down the middle and then slide a spoon in between the skin and the flesh. Note that the skin is not edible. You can eat it raw in a fruit salad, in a juice or smoothies.
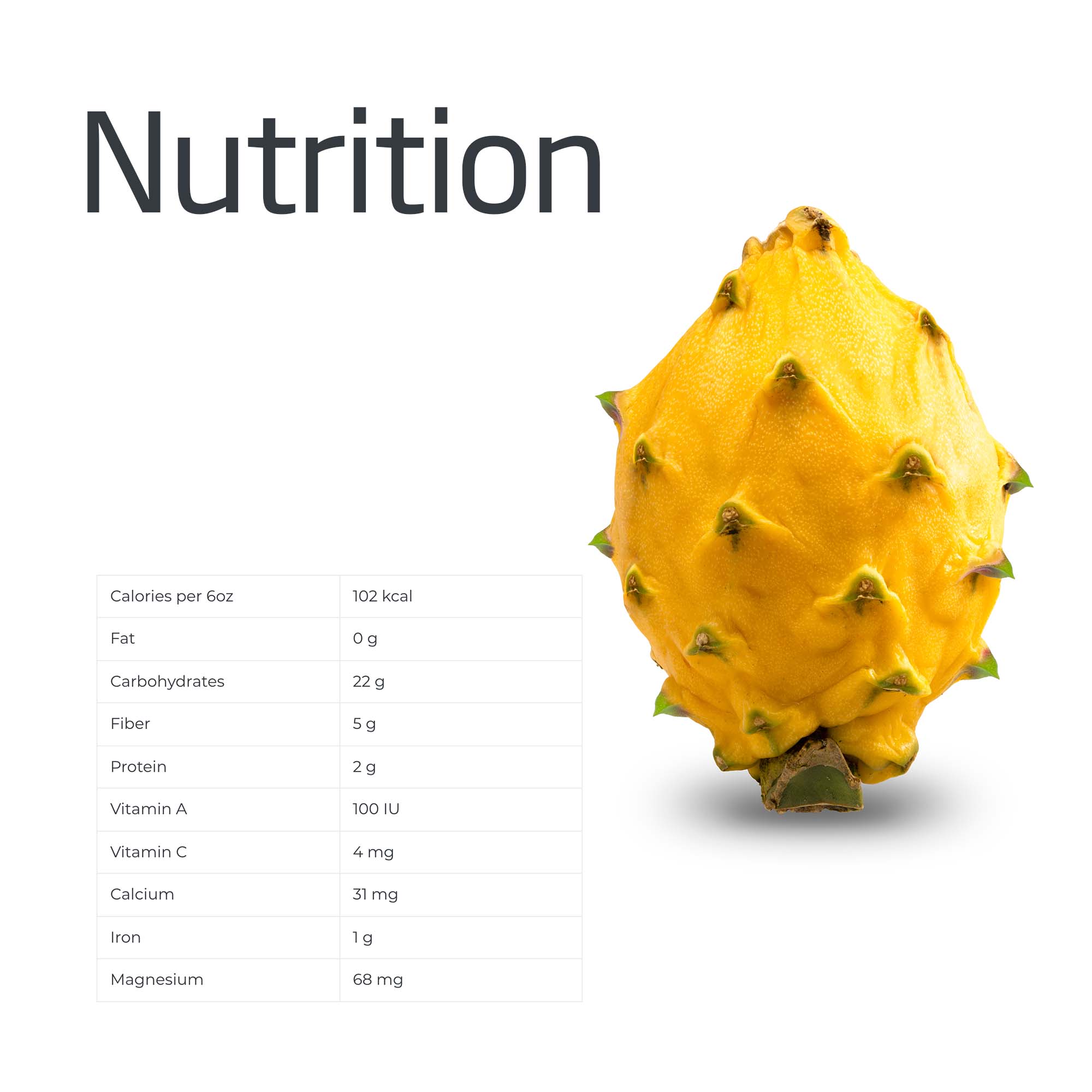
Nutritional Value
The yellow pitahaya is a good source of vitamins, proteins and it contains zero fats.
|
Calories per 6oz |
102 kcal |
|
Fat |
0 g |
|
Carbohydrates |
22 g |
|
Fiber |
5 g |
|
Protein |
2 g |
|
Vitamin A |
100 IU |
|
Vitamin C |
4 mg |
|
Calcium |
31 mg |
|
Iron |
1 g |
|
Magnesium |
68 mg |
SHIPPING
Choose your desired delivery date at the checkout, available delivery dates will be displayed at checkout stage. All orders are dispatched on a 24hr Next Working Day service. If no date is selected your order will be dispatched at the next available date.
We offer Free Next Working Day Delivery on all orders over £75 including our selection boxes.
Our shipping rates are as follows:-
England - £6.95
Scotland - £11.95
Northern Ireland - Not currently available
Customers are responsible for being present at the shipping address provided on the date selected at checkout. Exotic Fruits are not responsible for any missed or attempted deliveries that must be rearranged by the customer.
All orders are packed in cardboard boxes with a biodegradable packing pellets, straw, or hay to protect the fruit during transit.
RETURNS
Let's start by stating the obvious. Since our produce is perishable we cannot accept returns.
That said, we want every customer to be happy so we do offer vouchers, refunds and replacements at our sole discretion if your fruit has arrived inedible. If you would like to report an item which has become damaged or perished during transit, please:- We are not responsible for products that spoil if there is not someone to receive your delivery on the date that you request it, full tracking is provided and can be requested anytime after dispatch.